Digital Product Passport: What It Is and Why It Matters for Crypto and Blockchain
When you buy a pair of sneakers, a laptop, or even a bottle of wine, you’re not just paying for the product—you’re paying for its story. That story is now being recorded in a digital product passport, a blockchain-based record that tracks a product’s origin, materials, ownership, and lifecycle. Also known as digital twin, it’s turning supply chains from black boxes into open ledgers. Think of it like a vehicle’s VIN, but for everything—from your phone to your designer bag. And it’s not science fiction. The EU is already making it mandatory for electronics and textiles by 2026. Companies like LVMH and Adidas are using it to fight counterfeits. Meanwhile, crypto projects are building similar systems to verify NFT provenance and tokenized assets.
At its core, a digital product passport, a blockchain-based record that tracks a product’s origin, materials, ownership, and lifecycle. Also known as digital twin, it’s turning supply chains from black boxes into open ledgers. relies on three things: unique identifiers, immutable records, and smart contracts. Each item gets a unique ID—often tied to a QR code or NFC chip. That ID links to a blockchain where every step is logged: where the raw materials came from, who manufactured it, which warehouse held it, and who bought it. Smart contracts can even trigger actions—like auto-releasing a warranty claim or locking a stolen item’s functionality. This isn’t just about transparency. It’s about accountability. If a product fails, you know exactly where the flaw happened. If it’s stolen, you know who last held it. And if it’s fake, the system says so before you even pay.
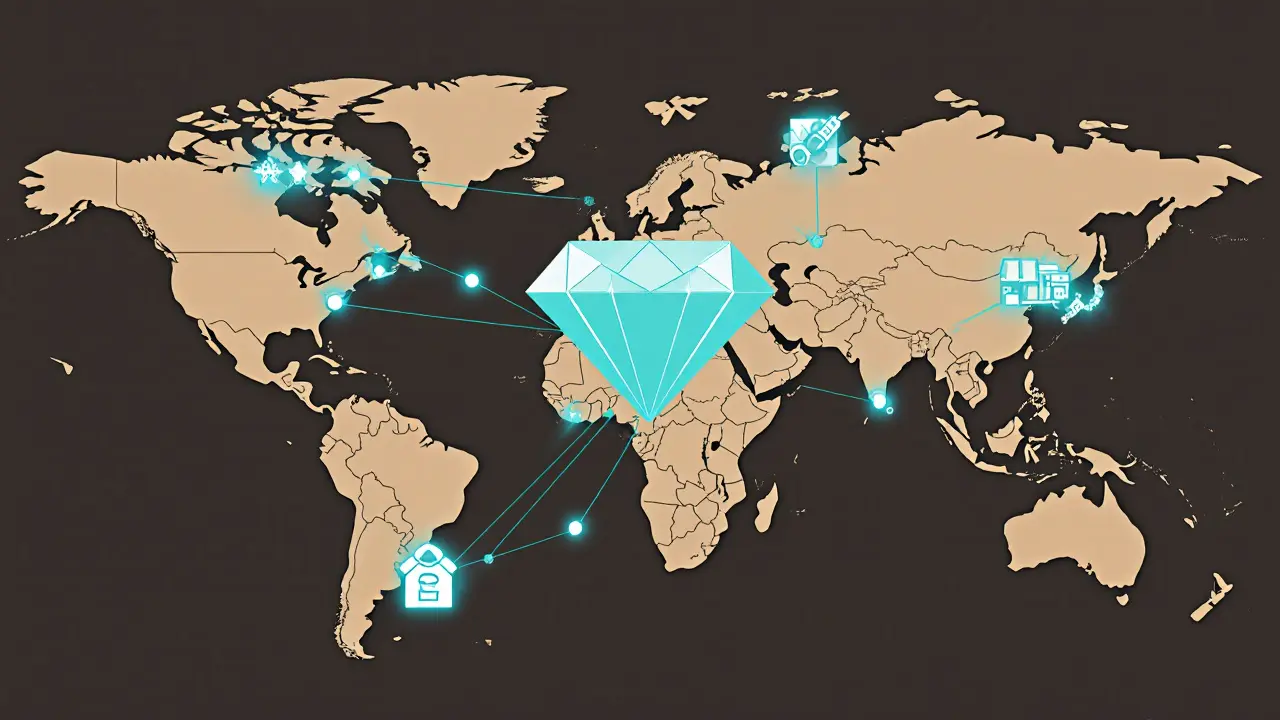
The connection to crypto and blockchain is direct. Projects like digital product passport are using the same tech behind Bitcoin and Ethereum to solve real-world problems. You’ll find parallels in how blockchain traceability, the use of distributed ledgers to verify the history and authenticity of physical and digital goods powers supply chain audits, how product authentication, the process of verifying that a physical or digital item is genuine and not counterfeit stops fake NFTs from flooding marketplaces, and how supply chain transparency, the ability to see and verify every step in a product’s journey from raw material to consumer helps brands meet ESG goals. Even crypto exchanges are starting to require proof of origin for tokenized assets—because if you can’t prove what you’re trading, you can’t trust it.
What you’ll find in the posts below aren’t theory pieces. They’re real examples: how a low-cap Solana token turned out to be a ghost project with no code, how a fan token on the Cronos chain has zero utility, and how blockchain’s ability to verify identity and ownership is being tested in places like Ecuador’s underground crypto market. These aren’t just crypto stories—they’re warnings about what happens when trust isn’t built on verifiable data. The digital product passport isn’t coming. It’s already here. And if you’re trading, investing, or just buying stuff online, you need to know how it works—or risk getting left behind.
NFTs are transforming global supply chains by providing unbreakable digital identities for products, reducing counterfeits, improving traceability, and automating payments. Learn how luxury brands, pharma, and logistics firms are using blockchain to build trust.
Categories
Archives
Recent-posts
Homomorphic Encryption for Privacy: How Encrypted Data Can Be Computed Without Being Seen
Feb, 10 2026

 Finance
Finance




